With the advent of the Internet of Things, many more devices are becoming connected to each other and the world around us which are performed by radio signals and wireless network and it’s also come up with the numerous threats.
This opens up our networks to vulnerabilities that could be exploited by hackers to gain access to our personal information or cause physical damage to infrastructure like cars, power plants, and even airplanes.
While we need to be concerned about cyberattacks against our computers and mobile devices, wireless network pose another threat. What are radio signals? And how can they affect your business’s cybersecurity?
Topics
How Cyber Attackers Exploit Radio Signals
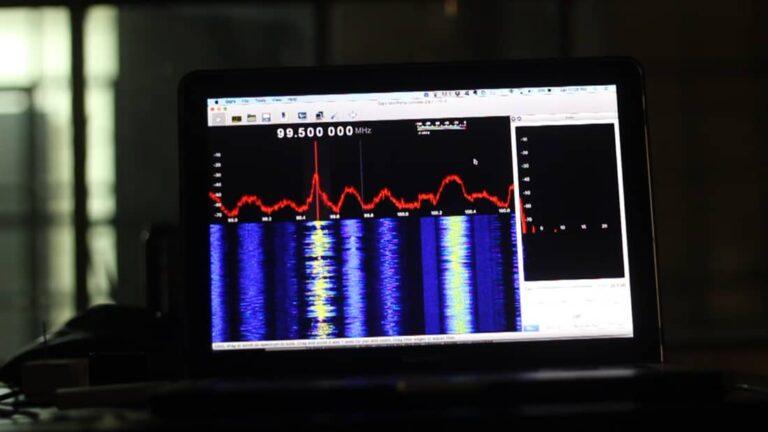
Radio signals are used for all sorts of things, including wireless communication. In fact, you may be familiar with some common types of radio signals such as AM/FM signals and Wi-Fi (2.4GHz). Most often these signals are completely safe—it’s not uncommon to have Wi-Fi routers installed in homes without anyone ever noticing them.
However, they can also be hijacked to gain unauthorized access to computer networks or other devices, and therefore need special protection.
Cyber security threats are not always considered because cyber attackers are constantly finding new ways to infiltrate and steal information. A recent example of a method that cyber attackers use to infiltrate targeted networks is through radio signals.
This process of using radio waves for attacks is known as RF-based (radio frequency) or wireless attacks. There are several steps that must be completed in order for a cyber attacker to succeed with an RF-based attack.
This is possible because many computers are programmed to regularly listen for radio signals in order to connect with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth networks without user intervention, which can leave them vulnerable to attacks when hackers send counterfeit radio signals – a phenomenon called a ‘man-in-the-middle’ attack.
Security reseachers at Ben Gurion University have discovered that radio signals can be used by cyber attackers to exploit network security vulnerabilities in wireless computer networks. Once hacked, computers are subject to being remotely controlled by an attacker.
Things You Need to Know About Cyber Security
Cyber security, a term that is associated with both radio signals and electronic communication these days, is one of those things you will want to understand, at least in theory.
Cyber security has become more important since wireless technology has advanced so quickly, thanks to society’s ever-increasing dependence on internet connectivity.
However, you may not be aware of how cyber threats are related to radio signals, like Wi-Fi. Here are three facts you need to know about cyber security when it comes to radio waves.
Threats to devices are growing. There are many threats to your cyber security as a result of radio signals transmission. Given that there is no clear definition of what constitutes an attack, it can be hard to know where you stand with regard to risks such as these.
Luckily, there are some general things you should know about cyber security when it comes to radio signals transmission in order for you to avoid potential problems. In addition, we have created a list of threats from radio signals transmission below so that you can see where potential problems might arise from using wireless technology on your computer or in your home.
Dangers from Radio signals
Radio waves are powerful, but they’re also very useful—for example, they’re used in Bluetooth technology.
But what if you could use radio signals to launch a cyber attack? Well, it turns out that there is some risk of a cyberattack via radio transmissions.
Here are some of the dangers of radio signals that we need to be aware of cyberattacks through electronic devices.
1. Stealing data from unprotected computers
2. connection to malware via hidden repeaters or spyware
3. Unintentional connections between wireless devices and nefarious users
4.Wireless access points controlled by others
5. Third-party control of networks or data centers (this includes poorly protected connections)
6. Unauthorized surveillance due to poorly secured cameras
How do you protect against these kinds of attacks?
What are other ways cyber attackers exploit radio signals?
We know that cyber attackers can exploit radio signals to steal data. But what other methods do they use?
Radio waves can travel through walls and doors. That makes them an effective way to get malicious code into computer systems, especially in healthcare facilities where sensitive patient data is stored.
Hackers will often try to access computers by sending radio signals that look like they’re coming from inside a building or hospital, even if they’re actually located miles away. And once those intruders gain a foothold on one machine, they can spread their malicious software throughout a network more easily than other methods of attack.
These man-in-the-middle attacks are designed to evade firewalls and other cybersecurity measures designed to keep networks safe. The attacker acts as a gateway between two legitimate parties while also launching attacks on either end of the connection.
Main Ways Cyber Attacks Occur through Radio Signals
Radio waves are a common way for hackers to infiltrate a network. This is because radio signals have no physical substance and can carry through almost any material. Hackers can use them to exploit gaps in cyber security. And sometimes, they just try them at random until something works.
Even your Wi-Fi router is vulnerable: it may be transmitting data without you knowing it. It’s hard to detect when a Wi-Fi signal has been hacked, making it difficult to protect against these kinds of threats – but here are some tips that can help with that.
- Don’t create weak passwords: Make sure all your accounts have strong passwords.
2. Hide important electronics: Don’t keep computers, routers, etc., where anyone could potentially see them from outside your home.
Ways To Prevent A Cyber Attack
The idea of cyber attacks has become so common in today’s digital world that it might seem unrealistic to think that an individual or a business won’t be affected by one. However, it is possible to minimize your risk of getting hacked.
Consider implementing these three tips on ways to prevent a cyber attack:
1. Get familiar with firewalls Firewalls are programs designed to detect malicious traffic within networks and stop them before they can get into a system.
2. Understand IP addresses In computing, an Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.
3. Secure Wi-Fi hotspots Many people believe wireless internet connections to be inherently more secure than their wired counterparts because information passes through air rather than along cables.
Despite being easy and convenient, free WiFi hotspots at restaurants and cafes could easily hide malware-infected computers seeking access.
secure your privacy and confidentiality from radio signals
These advanced features work together to strengthen defenses against hacking attempts through radio signals, ensuring a robust security system:
Detection of 2G/3G/4G/5G Signals:
- Identify and analyze different generations of mobile signals to spot potential vulnerabilities or unauthorized access.
Detection of DECT/Bluetooth/GSM/WLAN/WIFI/GPS:
- Identify various communication protocols, including wireless and Bluetooth technologies, offering broad coverage against potential threats.
3 Operation Modes (Search, Oscillograph, Security):
- Customize the device’s operations for specific needs, allowing searches, signal pattern analysis, and the implementation of enhanced security protocols.
Background Subtraction Function:
- Reduce interference by removing background signals, improving the accuracy of signal detection and lowering false positives.
4 Banks of Memory (2,000 signals per Bank):
- Store extensive signal data for analysis, providing historical information for threat assessment and incident response.
PDF Reporting – PC/MAC/Linux Compatible:
- Generate detailed reports in PDF format compatible with various operating systems for comprehensive analysis and documentation.
Acoustic Indication:
- Receive audible alerts for signal detection, ensuring real-time awareness and response to potential threats.
Probing Signal:
- Actively test and assess the security posture of the monitored environment using probing signals.
Antenna 1 – Frequency Range 10-2400 GHz:
- Cover a wide spectrum of frequencies to detect various signals and potential threats.
Antenna 2 – Frequency Range 2400-8000 GHz (High-Speed Channel):
- Extend coverage with a high-speed channel antenna for signals operating at higher frequencies.
Dynamic Range – Up to 70 dB:
- Achieve a high dynamic range for precise signal measurement, ensuring accurate detection and analysis.
High Sensitivity up to: -70 dBm (ANT 1) -50 dBm (ANT 2):
- Exhibit high sensitivity to detect even weak signals, enhancing overall security.
Built-in Frequency Meter – TURBO Frequency Identification:
- Use a built-in frequency meter for quick and accurate identification of signal frequencies, improving efficiency in threat analysis.
Overwatch RF Monitoring Protocols – Security Mode:
- Implement security-focused monitoring protocols for an enhanced level of protection, ensuring a proactive approach to potential threats.
These features collectively establish a strong defense mechanism against hacking attempts through radio signals, providing a comprehensive and adaptive security solution.